How to Replace TPMS Sensors at Home: Complete DIY Guide Without a Tire Machine
Are you dealing with a tire pressure warning light that won't go away? If your TPMS sensor battery is dying or the sensor has failed, you don't need expensive tire shop services. This comprehensive TPMS sensor installation guide will show you how to replace tire pressure sensors at home using common hand tools.
What is a TPMS Sensor and Why Do They Fail?
A tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) sensor is a small electronic device mounted inside your tire that monitors air pressure and sends radio frequency signals to your car’s computer. Each TPMS sensor contains a small watch battery that typically lasts 8-12 years or around 100,000-150,000 miles.
Common Signs of a Bad TPMS Sensor
- Tire pressure warning light stays on
- TPMS sensor fault message on dashboard
- Inconsistent tire pressure readings
- Warning light flashing then staying solid
Tools and Materials Needed for TPMS Sensor Replacement
Before starting your DIY TPMS sensor replacement, gather these essential tools:
Required Tools:
- Scissor jack (from your spare tire kit)
- Block of wood
- Valve core removal tool
- 11mm socket wrench (varies by vehicle)
- WD-40 or tire lubricant
- TPMS programming tool or OBD2 scanner
Optional Tools for Alternative Method:
- 6-8 foot 2×4 lumber
- Wood screws
- Air-powered die grinder or hacksaw (if stem spins)
Step-by-Step TPMS Sensor Installation Guide
Step 1: Prepare the Vehicle
- Park on level ground and engage parking brake
- Remove the wheel using your standard tire changing procedure
- Use valve core tool to remove valve core, releasing all air pressure
- Alternative: Let air out through valve stem if you don’t have a valve core tool
Step 2: Break the Tire Bead
This is the most crucial part of the TPMS sensor replacement process:
- Get your scissor jack from the spare tire compartment
- Place a block of wood on the tire sidewall to prevent damage
- Position the scissor jack on the wood block
- Jack “up” while the tire is on the ground – this pushes down on the sidewall
- Continue until you hear a “pop” – this is the bead breaking
Important Notes:
- This method works best on standard passenger car tires
- Light truck tires and low-profile tires are harder to break due to stronger sidewalls
- The wood block prevents sidewall damage during the process
Alternative Method Without Scissor Jack:
If your vehicle doesn’t have a scissor jack:
- Create a lever system using a 6-8 foot 2×4
- Secure a crosspiece to create a pry bar
- Use leverage to push down on the tire sidewall
- Apply steady pressure until the bead breaks
Step 3: Remove the Old TPMS Sensor
- Locate the sensor mounting nut (typically 11mm on Honda, varies by manufacturer)
- Unscrew the nut from outside the wheel
- Remove the sensor through the bottom of the wheel
- Be careful not to drop it into the tire
Troubleshooting Tip: If the valve stem spins with the sensor (common on Honda vehicles), you may need to cut the stem with a hacksaw or die grinder. Be extremely careful not to damage the tire sidewall.
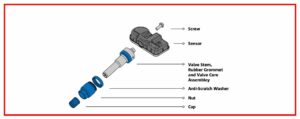
Step 4: Install the New TPMS Sensor
- Insert the new sensor from inside the wheel
- Install the new washer (included with sensor)
- Thread on the new nut from outside
- Tighten snugly but don’t over-torque – stems can break easily
- Replace the dust cap
Reseating The Tire Bead
Step 5: Prepare for Bead Seating
- Apply WD-40 or tire lubricant around the tire bead
- Position the wheel so tire weight helps with seating
- The ground helps pull the tire down onto the rim
Step 6: Inflate and Check
- Reinstall the valve core if removed
- Inflate to manufacturer specifications (check driver door jamb)
- Listen for the “pop” when bead fully seats
- Check for proper seating all around the tire
TPMS Sensor Programming and Reset Procedures
After installing new TPMS sensors, you must reprogram or retrain the system:
Understanding TPMS Sensor ID Numbers
Each TPMS sensor has a unique ID number that your car’s computer recognizes. When you install new sensors, the computer needs to learn these new ID numbers.
Programming Methods:
Option 1: TPMS Programming Tool
- Professional tools like the Autel TS501 ($220) plug into OBD2 port
- Read new sensor IDs and program them into the vehicle computer
- Most reliable method for non-clonable sensors
- Lifetime updates available from manufacturer
Option 2: Clonable Sensors
- Some aftermarket sensors can copy old sensor ID numbers
- Use cloning tool to transfer old ID to new sensor
- No computer reprogramming needed
- Check sensor specifications before purchasing
Option 3: Vehicle-Specific Learn Procedures
- Some vehicles have built-in learn modes
- Consult owner’s manual for specific procedures
- May involve drive cycles or button sequences
Cost-Saving Tips and Alternatives
DIY Battery Replacement Option
For mechanically inclined individuals, you can replace just the battery:
- Remove sensor back cover carefully
- Dig through silicone potting compound to find battery
- Desolder old battery and solder in new one
- Re-seal with silicone and reassemble
- Much cheaper but requires soldering skills
Cost Comparison
| Item | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| New TPMS sensors | ~$20–40 each |
| Replacement batteries | ~$3–5 each |
| Professional installation | $50–100 per sensor |
Why Complete Replacement Makes Sense
For 12-year-old vehicles with 150,000+ miles:
- Sensors endure constant vibration from potholes and road impacts
- Complete replacement provides peace of mind
- Relatively low cost compared to roadside assistance
- Avoid future failures of other sensor components
Important Considerations and Tips
Wheel Balance Maintenance
- Only break top bead – bottom stays sealed
- Wheel cannot rotate inside tire
- No rebalancing needed if done correctly
- Install similar weight sensor to maintain balance
Tire Type Considerations
- Standard passenger tires: Easiest to work with
- Light truck tires: Thicker, stronger sidewalls – more difficult
- Low-profile tires: Reinforced sidewalls – may require professional service
- Run-flat tires: Not recommended for DIY replacement
Band-Style TPMS Sensors
Older Ford and some other vehicles use band-style sensors:
- Mounted around wheel rim rather than valve stem
- May require complete tire removal
- Less common in modern vehicles
- Check manufacturer service procedures
When to Seek Professional Help
Consider professional TPMS sensor replacement if:
- Working with run-flat or low-profile tires
- Band-style sensors that require rim separation
- Multiple sensors failing simultaneously
- Lack confidence in DIY tire work
- Don’t have programming tools and sensors aren’t clonable
Troubleshooting Common TPMS Issues
TPMS Light Still On After Replacement?
- Check all sensor installations for proper seating
- Verify programming was completed successfully
- Drive 10-15 minutes to allow system initialization
- Check tire pressures are at specification
- Scan for additional fault codes
Sensor Programming Failed?
- Verify sensor compatibility with your vehicle
- Check programming tool is up to date
- Ensure strong OBD2 connection
- Try alternative programming method
- Consult vehicle-specific procedures
TPMS Sensor Maintenance and Lifespan
Extending TPMS Sensor Life:
- Maintain proper tire pressure to reduce sensor workload
- Avoid harsh impacts when possible
- Regular tire rotations help identify failing sensors early
- Address TPMS warnings promptly to prevent secondary issues
Expected Lifespan:
- Original equipment sensors: 8-12 years
- Aftermarket sensors: 5-10 years
- Battery life varies with climate and driving conditions
- Cold weather can accelerate battery drain
Conclusion
Replacing TPMS sensors at home is an achievable DIY project that can save significant money compared to professional installation. With basic hand tools and careful attention to the bead-breaking technique, most car owners can successfully complete this repair.
The key to success is patience during the bead-breaking process and having the proper programming tools for your specific vehicle. While the initial investment in a TPMS programming tool may seem high, it pays for itself quickly if you’re maintaining multiple vehicles or helping friends and family.
Remember that tire pressure monitoring systems are important safety features. Properly functioning TPMS sensors help prevent tire blowouts, improve fuel economy, and extend tire life. Don’t ignore TPMS warning lights – address sensor issues promptly for optimal vehicle safety and performance.
For vehicles with complex TPMS systems or if you’re uncomfortable with any part of this procedure, professional installation remains a viable option. The most important thing is ensuring your tire pressure monitoring system functions correctly to keep you safe on the road.
Related Topics: TPMS reset procedures, tire pressure sensor troubleshooting, automotive DIY repairs, wheel and tire maintenance, OBD2 programming tools