Symptoms of a Bad Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor) and What to Do
The oxygen sensor, or O2 sensor, is a small but very important part of your car. It checks how much oxygen is in the exhaust gases and helps the engine decide how much fuel to use. This keeps the engine running smoothly, saves fuel, and helps reduce pollution. If the oxygen sensor goes bad, it can cause a lot of problems. Let’s look at the most common signs and what they mean.
What Is an Oxygen Sensor (O2 Sensor)?
An oxygen sensor, also called an O2 sensor or lambda sensor, is a small but important part found in most cars and motorcycles. Its job is to measure how much oxygen is in the exhaust gases and send this information to the vehicle’s engine control unit (ECU).
The ECU uses this data to adjust the air-to-fuel ratio—which is how much air and fuel are mixed before burning in the engine. The perfect mix is 14.7 parts of air to 1 part of fuel, also known as the lambda ratio. This balance helps the engine run smoothly, saves fuel, and reduces harmful emissions.
Oxygen sensors are usually placed in the exhaust system, sometimes before and after the catalytic converter. If the air-fuel mix is off—either too rich (too much fuel) or too lean (too much air)—the engine won’t run well, and the catalytic converter won’t work properly. That’s why the oxygen sensor is so important—it helps keep everything working at its best.
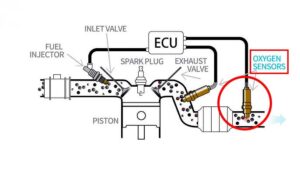
Where is the Oxygen Sensor Located?
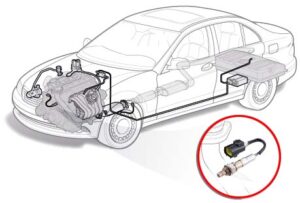
Oxygen sensors are typically located in a vehicle’s exhaust system, either before or after the catalytic converter. There are two main types of oxygen sensors:
- Upstream Sensor: Positioned before the catalytic converter, this sensor monitors the air-fuel ratio and helps the Engine Control Unit (ECU) adjust the fuel mixture for efficient combustion.
- Downstream Sensor: Located after the catalytic converter, this sensor checks if the converter is working properly and ensures that emissions meet standards.
In V-engines, there are usually two sensors on each side, one upstream and one downstream. These sensors work by detecting oxygen in the exhaust, helping optimize fuel efficiency and reduce harmful emissions.
9 Symptoms of a Bad Oxygen Sensor and How It Affects Your Car
Check Engine Light Turns On
One of the first signs of a bad oxygen sensor is the check engine light. It might come on for many reasons, but a faulty O2 sensor is a common one. You can scan your car for free at stores like AutoZone or NAPA. If you get error codes between P0150 and P0167, it usually means a problem with the oxygen sensor. Cars can have multiple sensors, so it’s important to find out which one is bad.
Engine Misfires
A misfire means the engine is not running smoothly. This can happen if the O2 sensor sends the wrong signal about the air-fuel mixture. If the mixture is too lean (not enough fuel), it can burn too slowly and cause backfires. If it’s too rich (too much fuel), the fuel might not burn at all. Both can cause misfires and even damage the catalytic converter.
Poor Fuel Economy
A bad oxygen sensor makes the engine use too much or too little fuel. This can lead to poor fuel economy, meaning your car uses more gas than it should. You might also smell gasoline from the exhaust or notice that your fuel gauge goes down faster than normal.
Black Smoke from the Exhaust
Black smoke, especially in diesel vehicles, can be a sign of a rich air-fuel mixture caused by a bad O2 sensor. It’s usually more noticeable when you press the gas pedal hard. But keep in mind, other issues like a dirty air filter or faulty injectors can also cause black smoke.
Weak Engine Performance
If your car feels slower or struggles to move, especially in first gear or when you press the gas pedal, the O2 sensor might be the issue. A wrong air-fuel mix can cause the car to lose power and perform poorly at both low and high speeds.
Hard to Start the Engine
When the sensor gives incorrect data, the engine might get the wrong amount of fuel at startup. This can make the engine crank longer or even fail to start, especially in the morning or when the engine is cold.
Rough Idle
If your car shakes or the engine sounds uneven when it’s idling, it could be because of a bad O2 sensor. It can cause misfires or weak engine firing, which leads to vibrations and irregular engine noise.
Failed Emissions Test
One of the oxygen sensor’s main jobs is to help control emissions. If it fails, your car will likely not pass an emissions test. You might also notice raw fuel or black smoke coming out of the exhaust.
Problems with the Catalytic Converter
A faulty O2 sensor can lead to misfires and unburnt fuel, which damage the catalytic converter. Sometimes it can even overheat and crack the inside of the converter. Replacing a catalytic converter is very expensive, so it’s best to fix the sensor before it gets worse.
How to Check if the Oxygen Sensor is Bad
There are two easy ways to check:
- Scan the Car – Use an OBD2 scanner to check for error codes like P0150 to P0167.
- Live Data – Use a scanner that shows live data. Start the car and look at how the O2 sensor responds when you press the gas. If the sensor’s readings don’t match the engine’s RPMs, it’s likely bad.
Cost to Replace an Oxygen Sensor
O2 sensors are not cheap. A new one costs between $80 to $150, and OEM parts for newer cars can be even more. Labor costs depend on the car and how stuck the sensor is, but expect to pay another $50 to $100 for labor. Altogether, the total cost can be around $200. If you replace it yourself, all you need is a special O2 sensor socket which costs under $10.
| Cost Item | Professional Replacement | DIY Replacement |
|---|---|---|
| O2 Sensor (New) | $80 – $150 | $80 – $150 |
| OEM Sensor (New Cars) | $150+ | $150+ |
| Labor Cost | $50 – $100 | $0 |
| Special Socket Tool | Included in labor | Under $10 |
| Total Estimated Cost | Up to $200+ | As low as $90 |
Conclusion
A malfunctioning oxygen sensor can lead to a variety of issues, from poor fuel efficiency and increased emissions to potential engine damage. Recognizing the symptoms of a bad O2 sensor early on, such as the Check Engine Light coming on, rough idling, or decreased fuel efficiency, can help you avoid costly repairs down the road. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to have your oxygen sensor inspected and replaced as needed. Regular maintenance and timely sensor replacements will not only improve your vehicle’s performance but also keep your engine running smoothly and reduce its environmental impact.